Identity and Access Management Guide
What is Identity and Access Management (IAM)?
Identity and access management (IAM) is a practice that ensures the right individuals have access to the applications and data they need and only to the applications and data needed. It is part of a robust organizational need for cyber security identity and access management, combining identity management and access management.
While this sounds straightforward, many organizations do not have a documented process for all the required aspects of a cyber security identity and access management practice, generally failing at defining access based on roles and being able to provision the access needed and only the access needed.
Need for IAM
Identity access management can be seen as a maturation needed by companies as they move beyond demonstrating internal compliance with data protection for financial audits to the need to secure a digital enterprise. Cyber security identity and access management programs become more critical as bad actors step up efforts to disrupt business and steal sensitive data and when the bad actors become institutionalized by governments and big businesses.
 This is why identity and access management have become such a critical need. While audit compliance demonstrates an organization’s understanding of who has access to sensitive financial data and whether the access was authorized according to policy, identity and access management ensures that only authorized users can log into a system or application and that the access they are granted is appropriate to their role.
This is why identity and access management have become such a critical need. While audit compliance demonstrates an organization’s understanding of who has access to sensitive financial data and whether the access was authorized according to policy, identity and access management ensures that only authorized users can log into a system or application and that the access they are granted is appropriate to their role.
Another reason why identity and access management has become critical, is organizations need to be more proactive about detecting and stopping intrusion before the bad actor gains access. Intrusion detection is a large component of identity access management solutions.
Despite its complexity, a robust cyber security identity and access management program is no longer an option in a digitally-based business. Security breaches, ransomware attacks, and other malicious attempts to gain access to secure data have become so prevalent that cyber security is a mandate. The costs of a breach are both tangible and intangible: costing millions in ransom or recovery costs, revenue loss due to lost trust or reputation, and heavy fines for non-compliance by regulators.
How Identity and Access Management Works
Cyber security identity and access management works by enabling organizations to develop a robust identity access management program using several approaches. Identity and access management components include:
Multi-Factor Authentication
The use of mobile devices, email, security tokens or biometrics to ensure the individual logging in is not an imposter.
Identity Management
The ability to validate that the user is still valid, as well as their role in the organization is a critical identity and access management component. It can include integration to HR systems for internal identity and access management programs as these systems are the most accurate in identifying the user as a current employee and validating their current role.
Access Management
Using roles to automatically assign appropriate rights to the user across all authorized applications during login while ensuring they can access only authorized functions and data. This is a core component of identity access management and generally includes single sign on (SSO) capabilities across applications.
Intrusion Detection
The use of algorithms to detect patterns that might indicate an unauthorized attempt at access and prevent them from gaining access.
Credential Management
A core component of identity and access management is the ability of a user to set up their login and multi-factor authentication and reset their password as needed.
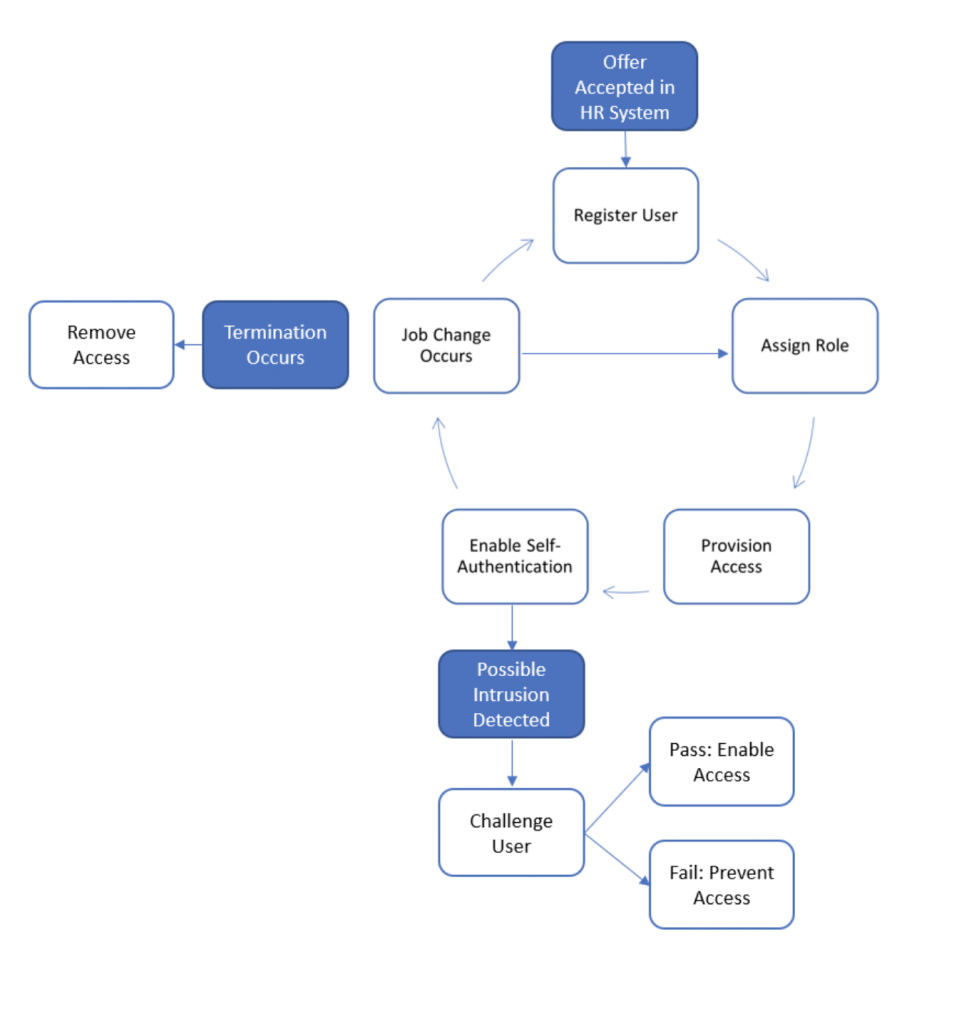
- With integration to HR systems, the access and identity management solution can create, update or disable the user account, enabling the organization to manage access throughout the employee’s lifecycle.
- As the HR system supplies trustworthy role (or title) information and employee’s status, this information is passed to the access provisioning component, which then provisions the appropriate roles within the appropriate systems and applications.
- The employee logs on and establishes their identity as the authorized user. If a potential intrusion is detected, a challenge is issued, and the user is provided with a mechanism to reset their password or is locked out.
- As individuals change roles in the organization, their access is automatically adjusted. They continue to access the systems until they are terminated, at which time their access is disabled.
A robust access and identity management solution combine these capabilities to enable an organization to onboard individuals and provide them with access: a visual example and explanation of how internal identity and access management works follows.
What is the Difference Between Identity Management and Access Management?
The difference between identity management and access management comes from their focus and the level of maturity within an organization.
Identity management is concerned with ensuring only authorized users gain access to a system or application. With identity management, the goal is to recognize an authorized user, determine their role in the organization, and validate their identity or challenge them and then validate their identity through a more secure method.
Access management ensures the person is then provided with the access defined for their role through internally developed and accepted access policies. These policies generally document the access to be provided based on the person’s role in the organization.
The primary difference between identity management and access management is that identity management determines the person’s identity and role, while access management provisions them with the appropriate access based on their role. Identity and access management together provide the controls needed by an organization to meet compliance and audit needs as well as helping them avoid provide unintended access to systems, applications, and data.
Another difference between identity management and access management is based on what they control: identity management ensures the validation of the individual, while access management controls the level of access delivered to them.
IAM – Control Types
A robust cyber security identity and access management solution leverages three primary control types:
Role-Based Access
Role-based access is a provisioning model that delivers the appropriate system and application access to an individual based on their title or organizational role rather than asking a manager to identify the access they need when they are hired. The manual basis of provision access based on a manager’s request has several deficiencies:
- As a control objective, manual authorization is time-consuming and difficult to prove due to its ad hoc nature, which requires an individual to provide documented proof of proper authorization.
- Provisioning methods may not always be accurate, especially when a “model-after” approach is using (in this approach, IT looks at the access Person X has currently and provides it to Person Y). One problem with this is that the two people may have slightly different roles, resulting in more than necessary access being granted.
- The mechanism also makes it difficult to adjust or revoke access completely when the person’s role changes or when they are terminated, raising additional control failures.
- Organizations need to build and maintain a robust access request process, constantly adjusting it as needs change.
By defining access based on each title family or functional role in an organization and automating the provisioning of access to individuals based on their role, the human factor is removed, and people are granted access accurately and efficiently by an identity access management solution.
Single Sign On (SSO)
As an authentication method provided by identity and access management solutions, single sign on enables a user to log and validate their identity once and then gain access to all the enterprises’ applications for which they are authorized. The identity access management solution passes their authorization between systems. Single sign-on enables a great user experience, especially when the employee crosses multiple systems from a single enterprise portal. It enables them to work functionally from a single pane of glass without knowing which application provides the service.
Multi-Factor Authentication
When single sign on is in play, it becomes even more critical than ever to control access by positively validating the user’s identity. Their username and password are no longer considered an effective control as a result of increased intrusion attempts and the level of access that a single password provides. Multi-factor authentication requires the user to enter a password and then further validates them through biometrics or by delivering a code to another device. Access is gained after the code is entered. The devices commonly used are a mobile phone or remote access token.
Benefits of Identity & Access Management
There are a number of tangible benefits to implementing an automated identity and access management solution:
- Compliance and audit: Role-based provisioning methods included in cyber security identity and access management programs mean that the access granted to a particular role needs to be authorized and proven only once: by documenting the system’s configuration. Once this is done, the need to annually audit granting of access is eliminated as the HR and access and identity management systems provide only the appropriate access. As each new system or application is brought online, access rights and roles are documented and approved.
- User experience: Single sign on provides an enhanced user experience as once they are authenticated, they gain access to enterprise applications easily. There is no longer a need to remember passwords across multiple systems, complicated further using different patterns for user IDs and password requirements. This simplicity makes it easier to remember ones’ password, making intrusion detection easier as well.
- Cost-effective administration: All user administration is performed automatically by the identity and access management solution, not by an army of access administrators. This lowers IT operational costs for administration, maintenance of request capabilities, and manual approval and audit processes.
- Staff retention: With a robust cyber security identity and access management practice, business employees no longer must spend time obtaining and managing their access. IT staff can focus on more challenging activities. Both of these add to staff retention.
- Enhanced security: Automation of repetitive manual tasks is generally more effective than relying on operations staff to monitor potential intrusion and manually provision access. By automating both of these areas, the rules are applied, and systems are monitored for intrusion 24×7. Additionally, no errors are made when provisioning access as this is also automated.
Leave IT to us
Our industry-leading solutions and services will allow you to focus on what matters most – your business.
Challenges and Risks of Implementing IAM
If all of this sounds too good to be true, perhaps it is due to the complexity of implementing a robust cyber security identity and access management program. Several areas must be documented to manage identity and access management effectively:
- Role/title consolidation: Organizations frequently have multiple titles that are functionally similar, and the challenge of implementing thousands of access profiles is daunting. Therefore, unless titles are consolidated, managing the volume of roles is a challenge.
- Role-based access planning: Once the roles are known, many IT organizations do not know and cannot tell what access should be provided to a particular role. While this may present a challenge, it is also a risk: that of providing more access to a role than it should have.
- Systems and applications are not the only access to manage: shared folders, shared mailboxes, even printers add complexity, especially if the business owner of the data or mailbox is not known.
- Difficulty in engaging the business to identify and approve the access each role should have can cause delays and inaccuracies in the profiles created. This is both a challenge and a risk.
- Fear of the time planning will take is a risk that must be mitigated by having a short- and long-term implementation plan in place.
Regardless of the implementation risks, the risks of not having a robust cyber security identity and access management practice and automated solution are far greater than the implementation risks, which can be mitigated with good planning and documentation and an agile-based implementation plan. Organizations should be ready to start with their most sensitive systems and data, gradually moving towards completion. Once momentum is gained, and the value of protecting the most critical systems is seen, it becomes easy to gain adoption for continuing to expand the program.
CG Technologies are experts at addressing the challenges of complex IAM situations, with in-depth experience in providing identity and access management solutions to a wide range of companies. Our expertise will protect your business, allowing you to mitigate the risks, control your costs, and allow you to concentrate on running your business. Contact us to learn more.